1.4.2.1 Docker Tips
1. Customize Your Own Docker Images: docker commit
For example, customize your own Ubuntu:22.04 by creating a new file named myversion.txt in the image's /etc directory to record the version number.
Customization:
Commit the modified Docker image (ID: 4ce35d7ed9b9):
Testing:
Refer to the video for more details.
2. Upload to Local Repository and Pull from HPC Node
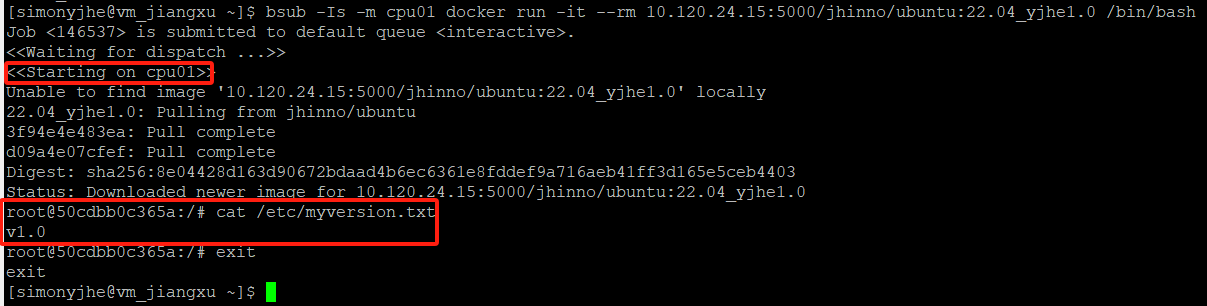
Upload to local repository: 10.120.24.15:5000/jhinno, and pull it down from an HPC node to run, then read the myversion.txt inside.
TAG:
PUSH:

Pull down and run on HPC node (cpu01), read the myversion.txt inside the container:
Refer to the video for more details.
3. Interact with Current Working Directory Data in Docker Container
Example:
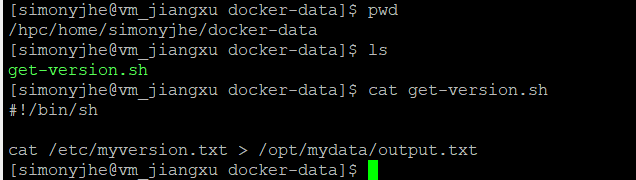
Map the current path: /hpc/home/simonyjhe/docker-data to /opt/mydata in the container.
Read the container's version and save it to /hpc/home/simonyjhe/docker-data/output.txt.
Preparation: The directory contains only one executable file, get-version.sh, which reads the version number of the previously customized Docker image and saves it to /opt/mydata/output.txt.
Submit to run on cpu01 node:
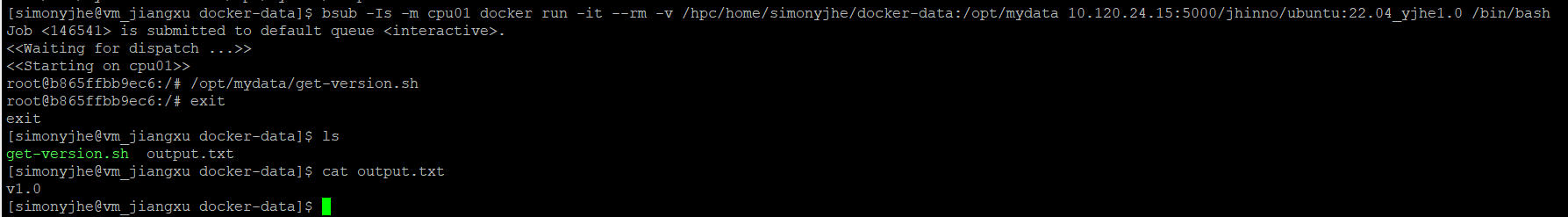
Parameter explanation:
--rm: Do not retain the container, delete upon exit.
-v /hpc/home/simonyjhe/docker-data:/opt/mydata: Map the working directory /hpc/home/simonyjhe/docker-data to /opt/mydata in the Docker container, enabling data interaction.
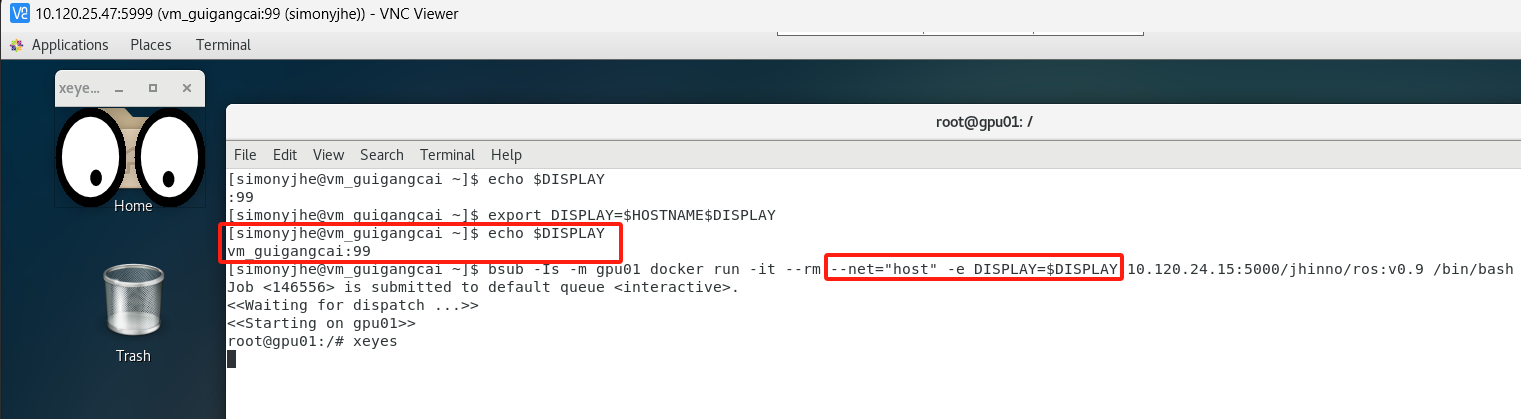
4. Display GUI from Docker Container Running on HPC Node
To display GUI from a Docker container running on an HPC node, specify two parameters:
--net="host"
-e DISPLAY="$DISPLAY"